Advanced hardware lab 8-2: identify cabling standards and technologies – Embark on a journey through advanced hardware lab 8-2, where we delve into the intricate world of cabling standards and technologies. This exploration promises to illuminate the significance of structured cabling, empowering you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of modern hardware infrastructure.
As we traverse this landscape, we will uncover the diverse array of cabling standards that govern the transmission of data and power, ensuring reliable and efficient communication. We will examine the distinct characteristics of various cabling types, exploring their advantages and limitations.
1. Cabling Standards and Technologies
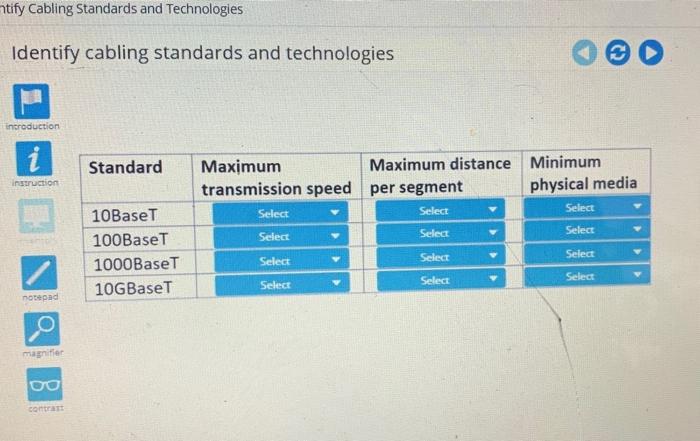
Cabling standards play a crucial role in advanced hardware labs, ensuring compatibility, performance, and reliability. They provide guidelines for the design, installation, and testing of cabling infrastructure, ensuring that it meets specific requirements and industry best practices.
Common cabling standards used in advanced hardware labs include:
- TIA/EIA-568-B:Defines the pinouts and cable specifications for twisted pair copper cabling, including categories 5e, 6, 6A, and 7.
- ISO/IEC 11801:International standard for generic cabling for customer premises, covering copper, fiber optic, and coaxial cables.
- ANSI/TIA-568.3-D:Specifies the requirements for balanced twisted-pair telecommunications cabling and components.
The selection of a cabling standard depends on factors such as the application, performance requirements, budget, and future expansion plans.
2. Types of Cabling
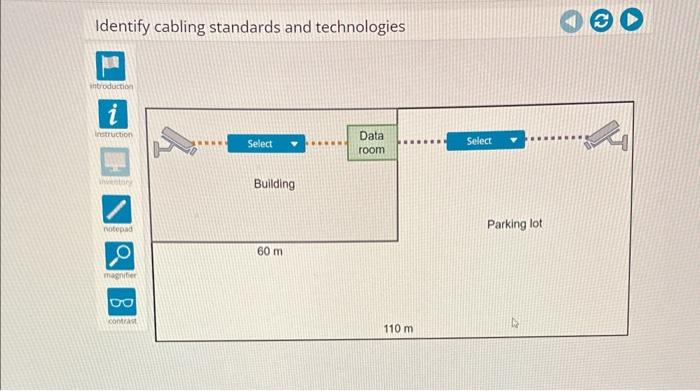
Different types of cabling are used in advanced hardware labs, each with its advantages and disadvantages:
Twisted Pair Cabling, Advanced hardware lab 8-2: identify cabling standards and technologies
Consists of multiple pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together, offering high bandwidth and noise immunity. Common types include Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat7.
Coaxial Cabling
Single copper conductor surrounded by an insulating layer and a braided or foil shield, providing high bandwidth and long-distance transmission.
Fiber Optic Cabling
Transmits data using light signals through optical fibers, offering extremely high bandwidth and low signal loss.
Wireless Cabling
Uses radio waves to transmit data, providing flexibility and mobility but with potential limitations in bandwidth and security.
3. Cabling Installation and Maintenance
Proper cabling installation and maintenance are essential for optimal performance and reliability:
Installation:
- Follow industry best practices and cabling standards.
- Use appropriate tools and techniques for cable termination and connection.
- Ensure proper cable routing and support to prevent damage.
Maintenance:
- Regularly inspect cables for damage or wear.
- Test cables using appropriate tools to identify potential issues.
- Document cabling infrastructure for future maintenance and troubleshooting.
4. Troubleshooting Cabling Issues: Advanced Hardware Lab 8-2: Identify Cabling Standards And Technologies
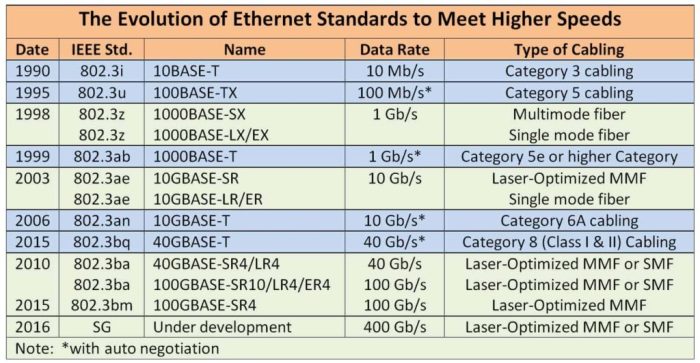
Common cabling issues include:
- Physical damage:Cuts, breaks, or crushes in cables.
- Termination problems:Improperly terminated or loose connections.
- Crosstalk:Interference between adjacent cables.
Troubleshooting involves:
- Visual inspection of cables and connections.
- Using cable testers to identify faults.
- Replacing or repairing damaged cables or connections.
5. Emerging Cabling Technologies
Advances in cabling technologies include:
- Category 8 cabling:Provides up to 40 Gbps bandwidth over copper cables.
- Fiber optic cabling with higher bandwidth:Offers even faster data transmission speeds.
- Wireless technologies with improved performance:Enhance mobility and reduce interference.
These technologies are being used in applications such as high-performance computing, data centers, and advanced networking.
Questions and Answers
What are the key factors to consider when selecting cabling standards?
Factors to consider include bandwidth requirements, transmission distance, electromagnetic interference, and environmental conditions.
How can I identify and resolve common cabling issues?
Common cabling issues can be identified through visual inspection, cable testing, and network monitoring. Troubleshooting involves isolating the affected segment, testing for continuity, and replacing faulty components.
What are the latest trends in cabling technologies?
Emerging cabling technologies include fiber optics, wireless connectivity, and power over Ethernet (PoE), offering higher bandwidth, improved flexibility, and enhanced energy efficiency.