The Law of Universal Gravitation Worksheet delves into the captivating world of physics, guiding you through the fundamental principles that govern the gravitational forces that shape our universe. This comprehensive resource unravels the intricacies of mass, distance, and the gravitational constant, providing a profound understanding of how these factors interplay to orchestrate the celestial ballet of planets, stars, and galaxies.
Throughout this exploration, we will uncover the historical tapestry woven by brilliant minds like Isaac Newton, whose groundbreaking discoveries laid the foundation for our comprehension of gravity. By examining practical applications in astronomy, engineering, and everyday life, we will illuminate the pervasive influence of this law in our world.
Key Concepts
Mass and Gravitational Force, Law of universal gravitation worksheet
Mass is a fundamental property of matter that determines the strength of its gravitational force. The greater the mass of an object, the stronger its gravitational pull.
Distance and Gravitational Force
The distance between two objects affects the strength of their gravitational force. The greater the distance, the weaker the gravitational force. This relationship is inverse square, meaning that the gravitational force decreases as the square of the distance increases.
Gravitational Constant
The gravitational constant (G) is a fundamental physical constant that appears in the mathematical equation for the Law of Universal Gravitation. It determines the strength of gravitational interactions between objects.
Mathematical Formulation
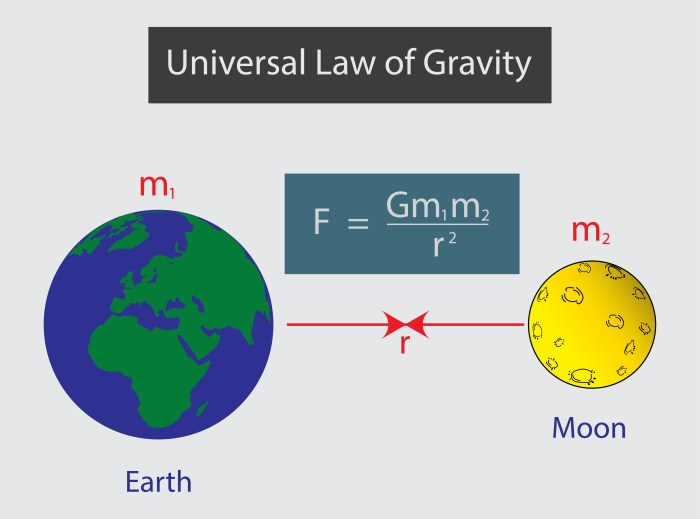
Equation for the Law of Universal Gravitation
The mathematical equation for the Law of Universal Gravitation is:
F = G
- (m1
- m2) / r2
where:
- F is the gravitational force
- G is the gravitational constant (6.674 x 10 -11N m 2kg -2)
- m1 and m2 are the masses of the two objects
- r is the distance between the centers of the two objects
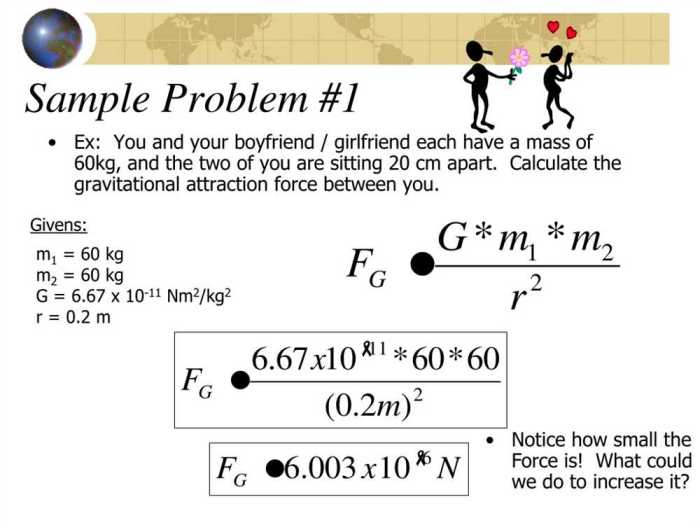
Using the Equation
To calculate the gravitational force between two objects, simply plug their masses and the distance between them into the equation. The result will be the magnitude of the gravitational force in newtons.
Applications: Law Of Universal Gravitation Worksheet

Astronomy
The Law of Universal Gravitation is used to calculate the gravitational forces between planets, stars, and other celestial bodies. This knowledge is essential for understanding the motion and interactions of these objects in space.
Engineering
Engineers use the Law of Universal Gravitation to design structures and machines that withstand gravitational forces. For example, bridges and buildings must be designed to withstand their own weight as well as the gravitational forces of wind and earthquakes.
Everyday Life
The Law of Universal Gravitation affects our daily lives in many ways. For example, it is responsible for the weight of objects on Earth, the tides in the ocean, and the trajectory of projectiles.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of the Law of Universal Gravitation?
The Law of Universal Gravitation is a fundamental law of physics that describes the attractive force between any two objects with mass. It governs the motion of celestial bodies, the formation of planetary systems, and even the everyday phenomena we observe, such as the falling of objects.
How does mass affect gravitational force?
The greater the mass of an object, the stronger its gravitational pull. This is why objects on Earth are pulled towards the Earth’s center, and why planets orbit the Sun.
What is the gravitational constant?
The gravitational constant is a fundamental physical constant that appears in the equation for the Law of Universal Gravitation. It determines the strength of the gravitational force between two objects.