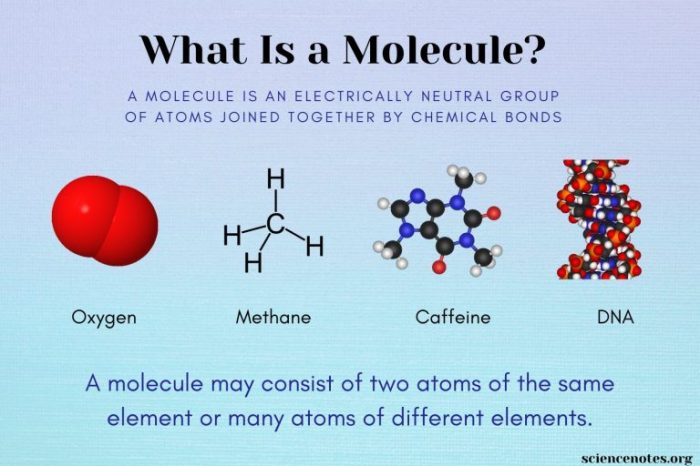
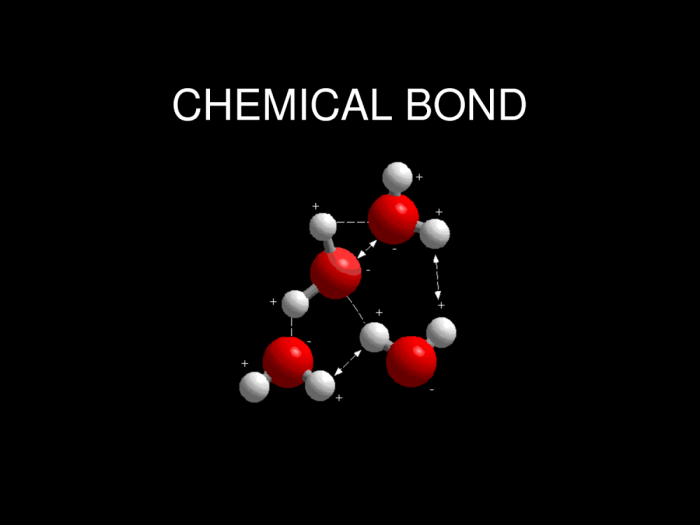
How are the building blocks of molecules like bricks? This analogy sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Just as bricks can be arranged in countless ways to create diverse structures, so too can atoms, the fundamental building blocks of molecules, be combined to form an astonishing array of substances with unique properties and functions.
This analogy between atoms and bricks provides a powerful framework for understanding the intricate world of molecules. By delving into the similarities and differences between these two seemingly disparate concepts, we gain a deeper appreciation for the fundamental principles that govern the behavior of matter at its most basic level.
Building Blocks of Molecules: How Are The Building Blocks Of Molecules Like Bricks
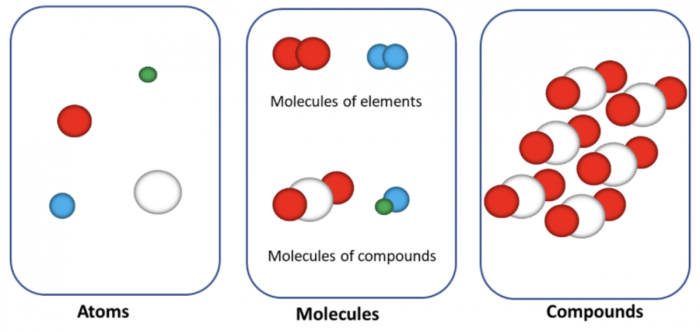
Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter, the smallest units of matter that retain the chemical properties of an element. They are composed of a nucleus, containing protons and neutrons, and electrons that orbit the nucleus.
Protons have a positive charge, neutrons are neutral, and electrons have a negative charge. The number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number, which identifies the element. The number of neutrons determines the isotope of the element.
Bricks in Construction
Atoms, like bricks in construction, can be arranged in different ways to create diverse structures. The arrangement of atoms within a molecule determines its shape and functionality.
Chemical bonds, like mortar in construction, hold atoms together. Covalent bonds form when atoms share electrons, ionic bonds form when electrons are transferred between atoms, and hydrogen bonds form when a hydrogen atom is bonded to a highly electronegative atom.
Properties of Building Blocks
Different atoms have unique properties, akin to the varying characteristics of different types of bricks. These properties influence the behavior and characteristics of the molecules they form.
For example, carbon atoms have four valence electrons, allowing them to form a wide variety of bonds. Oxygen atoms have two valence electrons, making them highly reactive and electronegative.
Molecular Architecture
Molecules exhibit different types of structures, analogous to various architectural designs. The arrangement of atoms within a molecule determines its shape and functionality.
Linear molecules, like carbon dioxide, have atoms arranged in a straight line. Branched molecules, like propane, have atoms arranged in a branched chain. Ring molecules, like benzene, have atoms arranged in a ring.
Chemical Reactions and Building Blocks, How are the building blocks of molecules like bricks
Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of building blocks (atoms). Energy is required to break bonds and form new ones, akin to the energy required to construct or remodel buildings.
In a combustion reaction, for example, the atoms of a fuel molecule are rearranged to form carbon dioxide and water molecules.
FAQ Explained
What are the fundamental building blocks of matter?
Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter. They are composed of even smaller particles called protons, neutrons, and electrons.
How do atoms combine to form molecules?
Atoms combine to form molecules when they share electrons. This sharing of electrons creates a chemical bond, which holds the atoms together.
How does the arrangement of atoms within a molecule affect its properties?
The arrangement of atoms within a molecule affects its shape, polarity, and reactivity. These properties, in turn, determine the molecule’s behavior and function.