Gum disease as it worsens progresses from to – Gum disease, a prevalent oral health concern, progresses through distinct stages, each characterized by unique signs, symptoms, and treatment considerations. This article delves into the evolution of gum disease, from its early manifestations to advanced periodontitis, providing a comprehensive overview of its progression and management.
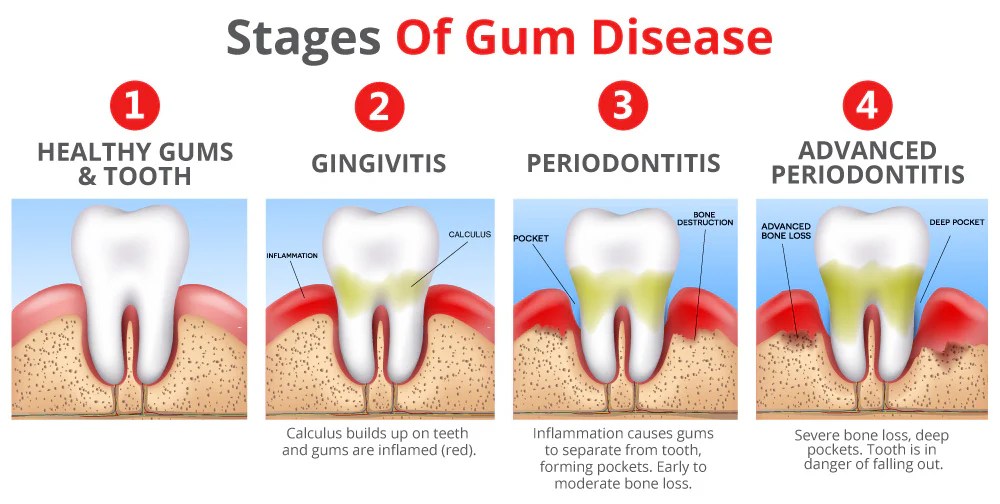
In the initial stages, gum disease presents with subtle signs such as bleeding gums and mild inflammation. As it progresses to moderate gum disease, symptoms become more pronounced, including receding gums, loose teeth, and persistent bad breath. Advanced gum disease, known as periodontitis, represents the most severe stage, characterized by significant tissue destruction, bone loss, and the potential for tooth loss.
Gum Disease: Progression and Management: Gum Disease As It Worsens Progresses From To
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common condition that affects the gums and the bones that support the teeth. It can range from mild to severe, and if left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss and other serious health problems.
Early-Stage Gum Disease
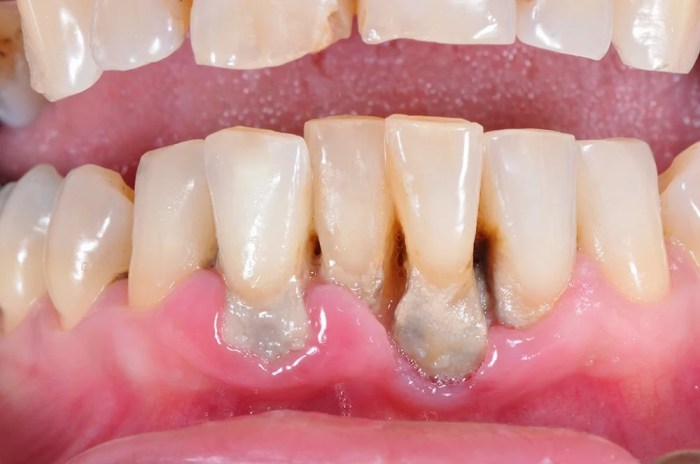
Early-stage gum disease, also known as gingivitis, is the mildest form of gum disease. It is caused by the buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. Plaque can irritate the gums, causing them to become red, swollen, and bleeding.
If gingivitis is not treated, it can progress to more severe forms of gum disease.
Moderate Gum Disease
Moderate gum disease, also known as periodontitis, is a more advanced form of gum disease. It is characterized by the destruction of the tissue that supports the teeth. This can cause the gums to recede, the teeth to become loose, and the formation of pockets of pus between the teeth and gums.
Periodontitis can be treated, but it can lead to permanent damage to the teeth and gums.
Advanced Gum Disease
Advanced gum disease, also known as severe periodontitis, is the most severe form of gum disease. It can cause significant damage to the teeth and gums, and it can lead to tooth loss. Advanced gum disease is often difficult to treat, and it can require surgery to remove the damaged tissue and restore the health of the gums.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the tissues surrounding the teeth. It is caused by the buildup of plaque and bacteria, and it can lead to the destruction of the bone that supports the teeth. Periodontitis is a serious condition that can lead to tooth loss and other health problems.
Treatment Options for Gum Disease, Gum disease as it worsens progresses from to
There are a variety of treatment options available for gum disease, depending on the severity of the condition. Non-surgical treatments include scaling and root planing, which is a deep cleaning of the teeth and gums, and antibiotics to kill the bacteria that cause gum disease.
Surgical treatments include flap surgery, which is a procedure to remove the damaged tissue and restore the health of the gums, and bone grafting, which is a procedure to replace the bone that has been lost due to gum disease.
Prevention and Management of Gum Disease
Gum disease can be prevented by practicing good oral hygiene, including brushing and flossing your teeth regularly, and visiting your dentist for regular checkups and cleanings. You can also reduce your risk of gum disease by avoiding sugary foods and drinks, and by quitting smoking.
User Queries
What are the early signs of gum disease?
Bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing, is an early indicator of gum disease.
Can gum disease be reversed?
Early-stage gum disease can often be reversed with proper oral hygiene and professional dental care. However, advanced gum disease typically requires more extensive treatment.
Is gum disease linked to other health conditions?
Research suggests a link between gum disease and certain systemic conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes, and stroke.