Step into the annals of scientific history with the Mendeleev Lab of 1869 Answer Key, a pivotal moment in the development of the periodic table. This comprehensive guide unveils the experimental setup, methodology, and groundbreaking discoveries that shaped our understanding of the elements.
Mendeleev’s lab was a crucible of innovation, where the periodic table emerged as a revolutionary tool for organizing and predicting the properties of elements. Join us as we delve into the legacy of this scientific masterpiece and explore its enduring impact on modern chemistry.
Mendeleev’s Lab of 1869: Mendeleev Lab Of 1869 Answer Key
In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev established a laboratory at the University of Saint Petersburg, which became a pivotal center for research and development in chemistry. Mendeleev’s lab played a crucial role in the development of the periodic table, one of the most significant scientific breakthroughs of the 19th century.
Experimental Setup and Methodology
Mendeleev’s lab was equipped with state-of-the-art apparatus for the time, including balances, spectroscopes, and furnaces. He employed a rigorous experimental methodology that involved:
- Measuring the atomic weights of various elements with precision.
- Studying the chemical and physical properties of elements and their compounds.
- Arranging the elements in order of increasing atomic weight, while considering their similarities and differences.
Through this systematic approach, Mendeleev identified patterns and relationships among the elements, leading to the development of the periodic table.
The Periodic Table
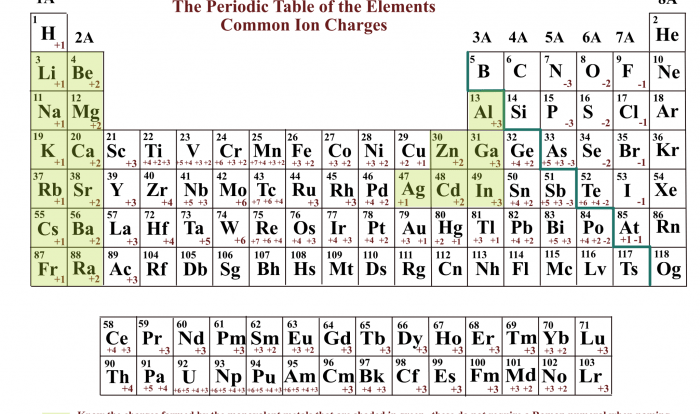
The periodic table, developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties.
Mendeleev’s periodic table was a revolutionary concept at the time, as it allowed chemists to organize and understand the vast number of known elements. It also provided a framework for predicting the properties of undiscovered elements.
Key Features of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table, Mendeleev lab of 1869 answer key
- The elements are arranged in horizontal rows (periods) and vertical columns (groups).
- The elements in each period have the same number of electron shells.
- The elements in each group have similar chemical properties.
- The table is divided into four blocks: s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block.
Predicting the Existence of Undiscovered Elements
One of the most remarkable features of Mendeleev’s periodic table was its ability to predict the existence of undiscovered elements. Mendeleev did this by leaving gaps in his table for elements that he predicted would be discovered in the future.
For example, Mendeleev predicted the existence of an element that he called “eka-silicon”. This element was later discovered and named germanium.
Mendeleev’s periodic table has been a powerful tool for chemists and has helped to advance our understanding of the chemical elements.
Modern Applications of Mendeleev’s Work
Mendeleev’s periodic table remains a cornerstone of modern chemistry and other scientific fields, providing a systematic framework for understanding and predicting the properties of elements and compounds.
One of the most important applications of the periodic table is in the field of materials science. By studying the periodic trends in properties such as electronegativity, atomic radius, and ionization energy, scientists can design and create new materials with specific properties tailored to particular applications.
For example, the development of high-strength alloys, lightweight composites, and advanced ceramics has been greatly aided by the use of the periodic table.
Predicting Chemical Reactions
The periodic table can also be used to predict the reactivity of elements and compounds. By understanding the electronic configurations of elements, scientists can determine their oxidation states and predict the types of chemical reactions they will undergo. This information is essential for understanding a wide range of chemical processes, including combustion, acid-base reactions, and redox reactions.
Organizing and Classifying Elements
The periodic table provides a systematic way to organize and classify elements based on their properties. This organization allows scientists to identify trends and patterns in the behavior of elements, which can help them understand the fundamental principles of chemistry.
For example, the periodic table can be used to classify elements as metals, non-metals, metalloids, and noble gases, each with its own unique set of properties.
Understanding Chemical Bonding
The periodic table can also be used to understand the nature of chemical bonding. By studying the electronic configurations of elements, scientists can determine the types of bonds they can form and the strength of those bonds. This information is essential for understanding the structure and properties of molecules and materials.
Limitations and Criticisms of Mendeleev’s Table
Mendeleev’s periodic table, while groundbreaking, had limitations. One was the placement of certain elements. For example, tellurium and iodine were placed in the same group, despite their differing chemical properties.Another limitation was the exclusion of noble gases. Mendeleev’s table did not include a place for these elements, as they were unknown at the time.
Subsequent Discoveries and Modifications
Subsequent discoveries and advancements have modified and expanded upon Mendeleev’s original table. The discovery of noble gases led to the addition of Group 18 to the table. The discovery of new elements, such as the actinides and lanthanides, also led to the expansion of the table.Additionally,
the development of quantum mechanics has provided a deeper understanding of the electronic structure of atoms, which has helped to explain the periodic trends in the properties of elements.
Mendeleev’s Lab: A Virtual Tour
Take a step back in time and explore the historic lab where Dmitri Mendeleev conducted his groundbreaking work on the periodic table. This virtual tour offers an immersive experience, allowing you to explore the equipment and experimental setup used by Mendeleev in his groundbreaking research.
As you navigate through the virtual lab, you’ll encounter interactive elements that provide insights into Mendeleev’s thought process and the significance of his discoveries. Discover the tools he used to organize and analyze data, and learn about the challenges and triumphs he faced along the way.
Interactive Elements
- Examine Mendeleev’s original periodic table, complete with handwritten annotations.
- Simulate the experiments Mendeleev conducted to determine the properties of different elements.
- Interact with a timeline that traces the evolution of Mendeleev’s ideas and the impact of his work.
Mendeleev’s Periodic Table: An Interactive Data Visualization
Mendeleev’s periodic table is an interactive data visualization that allows users to explore and learn about the elements. The table is organized by atomic number, atomic mass, and chemical reactivity. Users can filter and sort the elements based on these properties to see how they relate to each other.
Interactive Features
- Filter elements by atomic number, atomic mass, and chemical reactivity.
- Sort elements by atomic number, atomic mass, and chemical reactivity.
- View detailed information about each element, including its name, symbol, atomic number, atomic mass, and chemical properties.
- Compare elements side-by-side to see how their properties differ.
- Download the periodic table as a CSV or JSON file.
Detailed FAQs
What was the significance of Mendeleev’s periodic table?
Mendeleev’s periodic table revolutionized chemistry by organizing elements based on their atomic masses and chemical properties. It predicted the existence of undiscovered elements and paved the way for a deeper understanding of element behavior.
How did Mendeleev’s lab contribute to the development of the periodic table?
Mendeleev’s lab provided the experimental data and observations that formed the basis of his periodic table. Through careful experimentation, he determined the atomic masses and chemical properties of elements, enabling him to group them into a logical and predictive system.
What are the limitations of Mendeleev’s periodic table?
While Mendeleev’s periodic table was groundbreaking, it had limitations. It did not include noble gases, and the placement of certain elements was later found to be incorrect. Subsequent discoveries and advancements have modified and expanded upon Mendeleev’s original table.