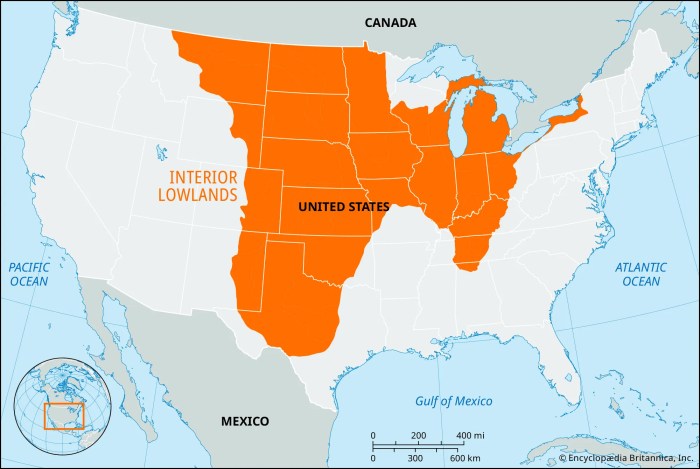
Map of the interior lowlands – Embark on a captivating journey through the Interior Lowlands, a realm of diverse landscapes and rich human history. This region unveils a tapestry of mountains, rivers, and lakes, shaping the terrain and influencing the lives of its inhabitants.
Delve into the climatic conditions that define the Interior Lowlands, discovering the interplay of temperature, precipitation, and humidity. Witness the flourishing vegetation that has adapted to these unique conditions, creating a vibrant ecosystem.
Geographic Features
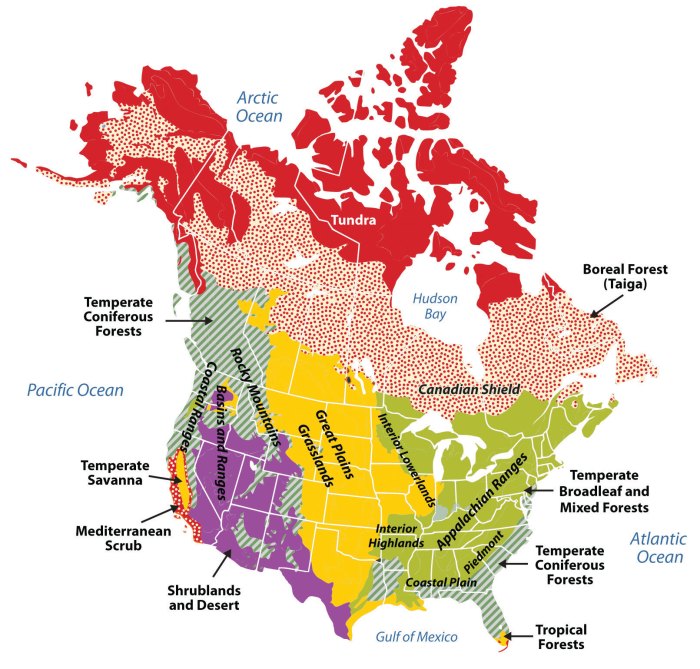
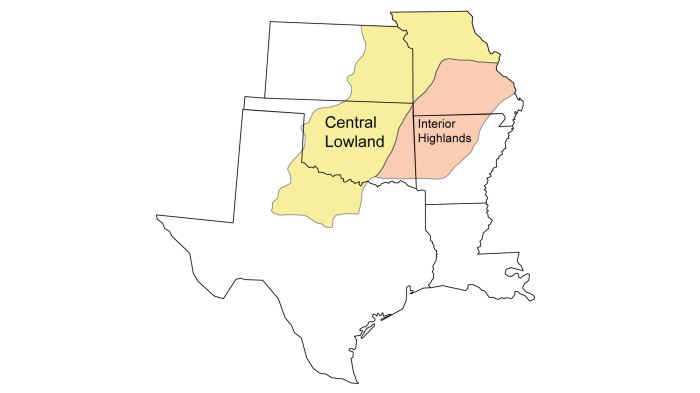
The Interior Lowlands are a vast region of flat to gently rolling terrain that stretches from the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico. The region is characterized by a number of major geographic features, including the Mississippi River, the Ohio River, and the Great Lakes.
These features have played a major role in shaping the landscape of the Interior Lowlands and influencing human settlement patterns. The Mississippi River, for example, has created a fertile floodplain that has been home to some of the most productive agricultural land in the United States.
The Ohio River has also been an important transportation route, connecting the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico.
Mountains
The Interior Lowlands are not home to any major mountain ranges. However, there are a few small hills and ridges in the region. These features are typically made up of sandstone or limestone and are often covered in forests.
Rivers
The Interior Lowlands are drained by a number of major rivers, including the Mississippi River, the Ohio River, and the Tennessee River. These rivers have played a major role in shaping the landscape of the region and have been important transportation routes for centuries.
- The Mississippi River is the largest river in North America. It flows from Lake Itasca in Minnesota to the Gulf of Mexico. The Mississippi River has a number of major tributaries, including the Ohio River, the Missouri River, and the Arkansas River.
- The Ohio River is the largest tributary of the Mississippi River. It flows from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania to Cairo, Illinois. The Ohio River has a number of major tributaries, including the Tennessee River, the Cumberland River, and the Wabash River.
- The Tennessee River is a major tributary of the Ohio River. It flows from Knoxville, Tennessee to Paducah, Kentucky. The Tennessee River has a number of major tributaries, including the Clinch River, the Holston River, and the French Broad River.
Lakes
The Interior Lowlands are home to a number of lakes, including the Great Lakes, Lake Erie, Lake Huron, Lake Michigan, and Lake Superior. These lakes are a major source of fresh water for the region and are also popular tourist destinations.
- The Great Lakes are a system of five lakes that are located on the border between the United States and Canada. The Great Lakes are the largest freshwater lakes in the world.
- Lake Erie is the fourth-largest of the Great Lakes. It is located between the states of Ohio, Pennsylvania, and New York.
- Lake Huron is the second-largest of the Great Lakes. It is located between the states of Michigan and Ontario.
- Lake Michigan is the third-largest of the Great Lakes. It is located entirely within the state of Michigan.
- Lake Superior is the largest of the Great Lakes. It is located between the states of Michigan, Wisconsin, and Minnesota.
Climate and Vegetation
The Interior Lowlands experience a humid continental climate, characterized by hot, humid summers and cold, snowy winters. Temperatures range from an average high of 85°F (29°C) in July to an average low of 15°F (-9°C) in January. Precipitation is abundant throughout the year, averaging around 40 inches (100 cm) annually.
The region is prone to severe thunderstorms and occasional tornadoes.
Vegetation
The vegetation of the Interior Lowlands is primarily deciduous forest, dominated by oak, maple, and hickory trees. These trees have adapted to the region’s climate by developing broad leaves that maximize sunlight absorption during the short growing season. In addition, their leaves turn vibrant colors in the fall before dropping, allowing them to conserve water during the cold winter months.
Navigating the intricate terrain of the interior lowlands requires a map, but if you’re preparing for a different journey, like the BMV practice test for St. Thomas , a different kind of map might be more useful. However, when it comes to exploring the vast interior lowlands, a detailed map remains indispensable, guiding you through the meandering rivers and rolling hills.
Natural Resources
The Interior Lowlands region boasts a wealth of natural resources, including minerals, timber, and water.
Minerals such as coal, iron ore, copper, lead, and zinc have been extensively mined in the region, contributing significantly to the development of industries and infrastructure. Coal mining, in particular, has played a pivotal role in the region’s energy production and economic growth.
Timber
The Interior Lowlands is also home to vast forests, providing a rich source of timber. The region’s forests have been sustainably managed over time, ensuring a continuous supply of timber for construction, furniture making, and other industries.
Water, Map of the interior lowlands
Water resources are abundant in the Interior Lowlands, with numerous rivers, lakes, and aquifers. These water resources support agriculture, industry, and recreation, contributing to the overall economic and environmental well-being of the region.
Human History
The interior lowlands have been inhabited by humans for thousands of years. The earliest inhabitants were nomadic hunter-gatherers who lived in the region’s forests and prairies.
Around 1,000 years ago, the first permanent settlements were established in the interior lowlands. These settlements were located along the major rivers and were based on agriculture. Over time, the region’s population grew and the settlements became larger and more complex.
Agriculture
Agriculture has been a major part of the human history of the interior lowlands. The region’s fertile soils and abundant water resources have made it ideal for growing crops. The most important crops grown in the region are corn, soybeans, and wheat.
Industry
Industry has also played a major role in the human history of the interior lowlands. The region is home to a number of major cities, including Chicago, Detroit, and St. Louis. These cities have been centers of manufacturing, transportation, and finance.
Impact of Human Activities on the Environment
Human activities have had a significant impact on the environment of the interior lowlands. The conversion of forests and prairies to agriculture and industry has led to the loss of habitat for many plant and animal species. The pollution of rivers and lakes has also harmed the region’s aquatic ecosystems.
Ways in which People Have Adapted to the Region
The people of the interior lowlands have adapted to the region’s climate and environment in a number of ways. They have built homes that are designed to withstand the region’s extreme temperatures. They have also developed agricultural practices that are suited to the region’s soil and climate.
Economic Development: Map Of The Interior Lowlands
The interior lowlands have been the center of economic activities since the early days of settlement. Agriculture, mining, and tourism have all played a significant role in the development of the region.
Agriculture is the primary economic activity in the interior lowlands. The fertile soils and favorable climate make the region ideal for growing a variety of crops, including corn, soybeans, wheat, and cotton. The region is also home to a large number of livestock, including cattle, hogs, and poultry.
Mining is another important economic activity in the interior lowlands. The region is rich in mineral resources, including coal, oil, and natural gas. These resources have been a major source of wealth for the region and have helped to fuel the growth of the economy.
Tourism is a growing economic activity in the interior lowlands. The region is home to a number of natural attractions, including the Great Lakes, the Mississippi River, and the Ozark Mountains. These attractions draw tourists from all over the world and contribute to the economic development of the region.
Cultural Heritage
The interior lowlands have a rich cultural heritage that has been shaped by the diverse groups of people who have inhabited the region over the centuries. These groups include Native American tribes, European settlers, and African Americans. Each group has contributed to the region’s unique cultural traditions, beliefs, and languages.
The cultural heritage of the interior lowlands has been preserved and passed down through generations through a variety of means, including oral tradition, music, dance, and art. Many of the region’s traditional cultural practices are still alive today, and they continue to play an important role in the lives of the people who live there.
Languages
The interior lowlands is home to a diverse range of languages, reflecting the region’s rich cultural history. Native American languages, such as Sioux and Cherokee, are still spoken by many people in the region. European languages, such as English, Spanish, and French, are also widely spoken.
In addition, there are a number of Creole languages, such as Gullah and Louisiana Creole, that are spoken in the region.
Traditions
The interior lowlands is home to a number of traditional cultural practices, including music, dance, and art. Music is an important part of life in the region, and there are many different styles of music that are popular, including blues, country, and gospel.
Dance is also an important part of the region’s culture, and there are many different types of dance that are popular, including square dancing, clogging, and line dancing.
Beliefs
The interior lowlands is home to a variety of religious beliefs, including Christianity, Islam, and Judaism. Christianity is the most common religion in the region, and there are many different denominations of Christianity that are represented. Islam is also a significant religion in the region, and there are a number of mosques located throughout the interior lowlands.
Judaism is also practiced by a small number of people in the region.
FAQ Summary
What are the major geographic features of the Interior Lowlands?
The Interior Lowlands encompass a diverse range of geographic features, including the Appalachian Mountains, the Mississippi River, and the Great Lakes.
How has the climate of the Interior Lowlands influenced human settlement?
The temperate climate and abundant water resources have made the Interior Lowlands a prime location for human settlement and agriculture.
What are the key natural resources found in the Interior Lowlands?
The Interior Lowlands are rich in natural resources, including coal, oil, natural gas, and timber.